What is a Procurement Value?- Definition
Procurement value in purely economic terms is about more bang for the buck where “bang” is the utility the business gets from supplier products/services, divided by the dollars (i.e., spend), which then decomposes to activity vs. cost, and then cost decomposes again down to price and non-price costs.
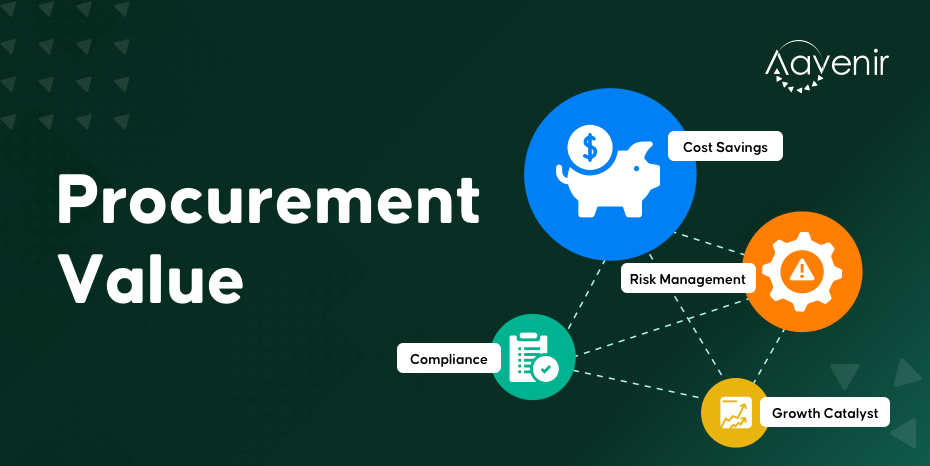
Understanding Procurement Value
In most organizations, cost savings are a primary performance measure.
Few executives and supply chain professionals would argue against that; spend visibility, good data, and control are the basics of procurement, after all.
But value can be delivered far beyond savings. Procurement staff has an essential role in contributing to their firm’s competitive advantage in areas as diverse as risk management, internal efficiencies, and even staff retention.
Five ways to create value in procurement
The role of procurement has changed. No longer is it just about purchasing goods and services, but it’s about ensuring operations run smoothly all year round. This means establishing requirements, researching the market, evaluating vendors, negotiating contracts, and managing risk are critical. Here are five ways procurement executives can gain value in their organizations.
1. Cut costs
All businesses want to reduce their costs without damaging their profit margins, but how is this achieved? By sourcing suitable suppliers, procurement staff actively help reduce their company’s outgoing costs and operational risks. However, finding reliable data and insight on potential suppliers is often expensive and takes time.
2. Drive innovation
Procurement professionals hold a prominent position within a business. They are the people that choose which suppliers to work with, and their choices often define their organization’s possible overall supply chain. By choosing suppliers that add value, procurement teams can place their company in a better overall position.
3. Leverage good data
There is a difference between collecting as much data as you can and basing decisions on high-quality supply chain data. A complex supply chain that involves product development, engineering, packaging, delivery, sales, forecasting, and more, utilizing data correctly creates insights that drive revenue and scales efficiency.
4. Drive growth in new markets
The best opportunities for value growth are often found outside established markets and supply chains. Previously untapped markets are often full of eager companies seeking to innovate and develop at an increasing rate. However, moving into the unknown requires a lot of research, knowledge, and assurance.
5. Help with CSR compliance.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a significant area of focus in business. The reputational damage that can come from non-compliance within an area of CSR, such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals, can often be irreparable because of its business supply chain. As a result, a detailed pre-qualification process is crucial for procurement professionals.
Explore Additional Resources to Know More



