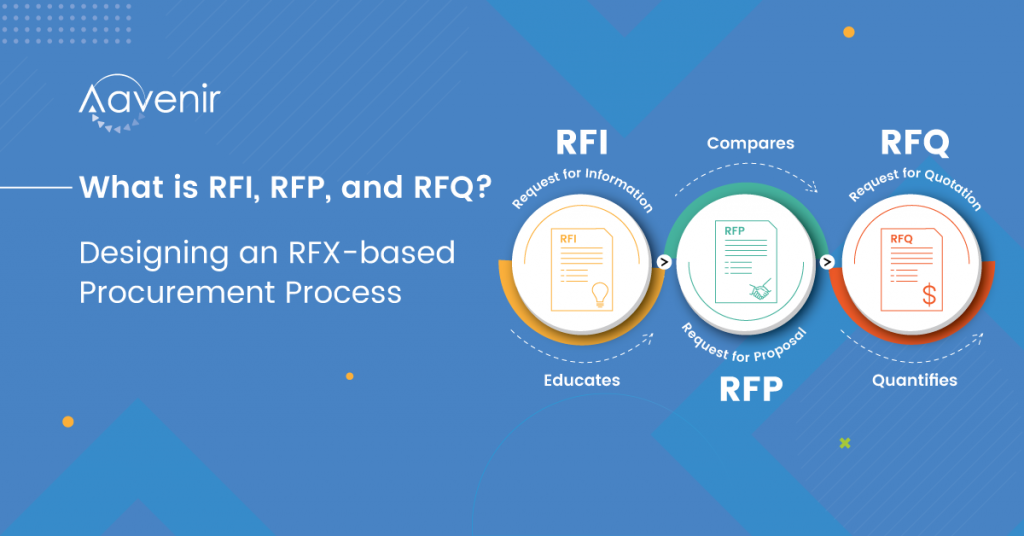
What is a Request For Proposal (RFP)?- Definition
A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that solicits proposals, often made through a bidding process, by an agency or company interested in procuring a commodity, service, or valuable asset, to potential suppliers to submit business proposals. It is introduced early in the procurement cycle, either at the preliminary study or procurement stage.

Understanding Request For Proposal (RFP)
RFPs are used for complex projects, often requiring several sub-contractors. They describe the organization issuing the RFP, the project’s scope being undertaken, and the criteria for evaluating entries. They also outline the bidding process and the contract terms.
The requests include a statement of work describing the tasks to be performed by the winning bidder and the timeline for finishing the job.
RFPs also advise bidders on preparing proposals, with specific guidance on how the bids should be formatted and presented. They generally include instructions on what information the bidder must consist of and the desired format.
Key Takeaways
- A request for proposal (RFP) is a project announcement posted publicly by an organization indicating that bids for contractors to complete the project are sought.
- The RFP defines the project for the company that issues it and the companies that respond to it.
- The RFP describes the project, its goals, and the organization sponsoring it and outlines the bidding process and contract terms.
- RFPs are used by most government agencies and many private companies and organizations.
- The alternative is a less formal process that may fail to identify the best vendor and the best plan for accomplishing a project.
Benefits of a Request for Proposal (RFP)
An RFP is, in part, an advertisement. It announces that a project is proceeding and opens the door to qualified candidates or suppliers who can get the job done.
In government, the RFP is adopted to ensure that cronyism is removed as a factor in rewarding contracts. It also opens up the process to competition, which is expected to keep project costs lower.
The alternative to an RFP is a less formal process requiring a project manager to research and identify potential vendors for a project. Depending on how exhaustive the search is, the possible responses can be limited. New vendors and innovative answers may be less likely to be uncovered.
Requirements for a Request for Proposal (RFP)
Government agencies or other entities may be required to issue requests for proposals to provide complete and open competition and to drive down the cost of a solution. Accepting a proposal that is most responsive to specifications may not always mean the lowest-priced bid.
Skillfully creating a request for proposal can ensure the success or failure of the resulting solution. If the specified requirements are too vague, the bidder may not design and implement an adequate explanation for the problem. If the conditions are too detailed and restrictive, the bidders’ innovation may be limited.
The RFP process begins with drafting a request for proposal. Bidders review the solicitation and submit suggestions for improvement. After implementing feedback, the final request for proposal is issued. Bidders then submit their proposals.
The customer narrows the selection down to a small group of bidders and enters pricing and technical details negotiations. The customer may ask the remaining bidders to submit a best and final offer before awarding a contract. The contract is then presented to the company providing the best solution to the issue.
Explore Additional Resources to Know More