What is Invoice Matching?

Invoice matching is a method in accounts payable that checks and compares information on the purchase order (PO) with information on the vendor invoice and product receipts.
When a company decides to use goods or services from a particular vendor, it issues a purchase order with specific requirements. For example, the buying organization gives a product receipt upon delivery of the requisitioned goods or services. The seller then raises the invoice for payment clearance, which is when invoice matching occurs.
Invoice matching ensures no mistakes or discrepancies between the PO and the invoice. It enables speedier settlement and reduces the risk of vendor fraud and payment for fake invoices.

What is an Invoice Exception?
A deviation (also known as an invoice exception) arises when there is a discrepancy between the invoice data and the validating papers, such as the PO or the goods/product receipt.
Identifying and reconciling invoice exceptions can be daunting for Accounts Payable (AP) teams. Therefore invoice exceptions should be evaluated to see whether they are within tolerance limits and should be reverted to the vendor for adjustments if any.
Minor fluctuations in percentages or quantities in an invoice are referred to as tolerance levels. Invoices that exceed tolerance thresholds are placed “on hold” and sent to the vendor for correction.
Deviations can be of two types – Quantity and Price
- Quantity deviation: refers to the difference between the quantity or number of goods on the PO and the invoice.
- Price deviation: refers to the difference between the cost specified in the PO and the amount specified in the invoice.
When a deviation is discovered during the invoice matching process, investigate if this deviation is acceptable or contact the vendor to rectify the inaccuracies on the invoice.
According to Ardent Partners’ State of ePayables Report, 45% of organizations consider exceptions the most challenging accounts payable issue.
Unfortunately, deviations are a significant concern. According to the same analysis, the average invoice exception rate among surveyed businesses in 2021 was 22.5%.
Why Is Invoice Matching Important?
Invoice matching is a complex but critical process in business accounting since it ensures purchase accuracy. Accuracy applies to both the client and the vendor in this way. For example, invoice matching guarantees that the company, as a client, makes appropriate payments to its vendors and that those payments are documented correctly in the internal accounting process.
Invoice matching further emphasizes the vendor’s responsibilities by assuring purchase order compliance. In both cases, invoice matching aids in fraud detection by avoiding unethical manipulation of the purchase process.
What Happens When Invoice Matching Finds an Exception?
Suppose invoice matching finds a discrepancy or exception. In that case, the purchased item will be marked, and accounting staff will launch an investigation to determine whether the exception falls within the company’s “tolerance.” If it exceeds the company’s tolerance, the accounting team will hold on to the invoice, and the vendor will be notified.
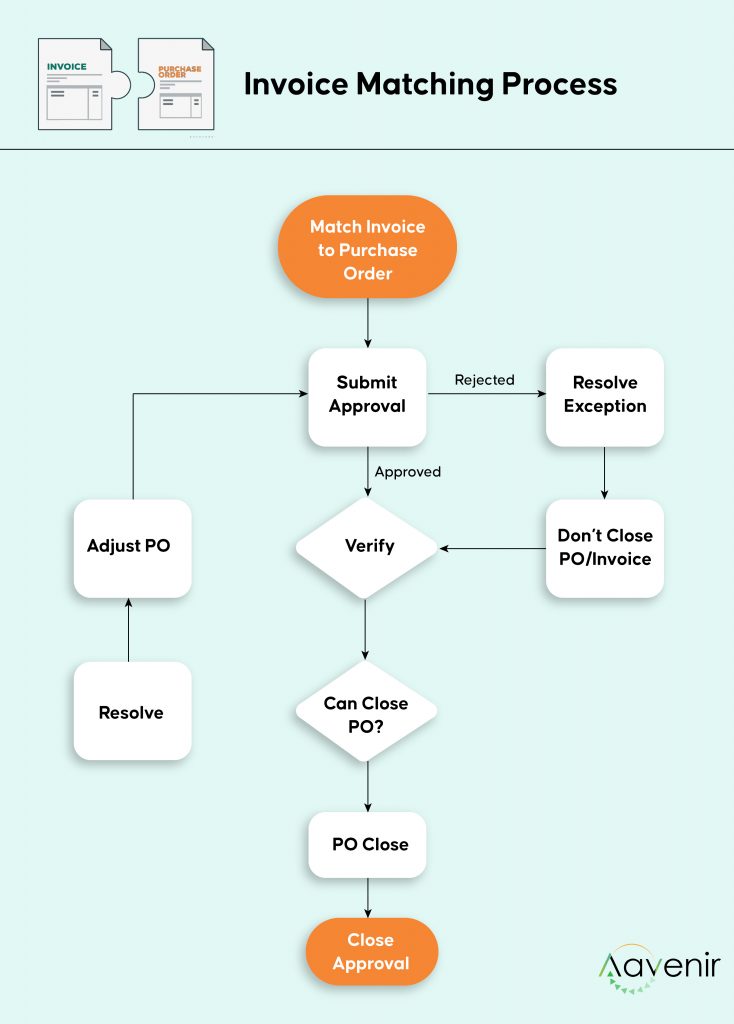
How is Invoice Matching Performed?
Invoice matching can be performed in several ways. First, it is carried out at several levels or tiers. Each successive tier requires a higher quantity of documents.
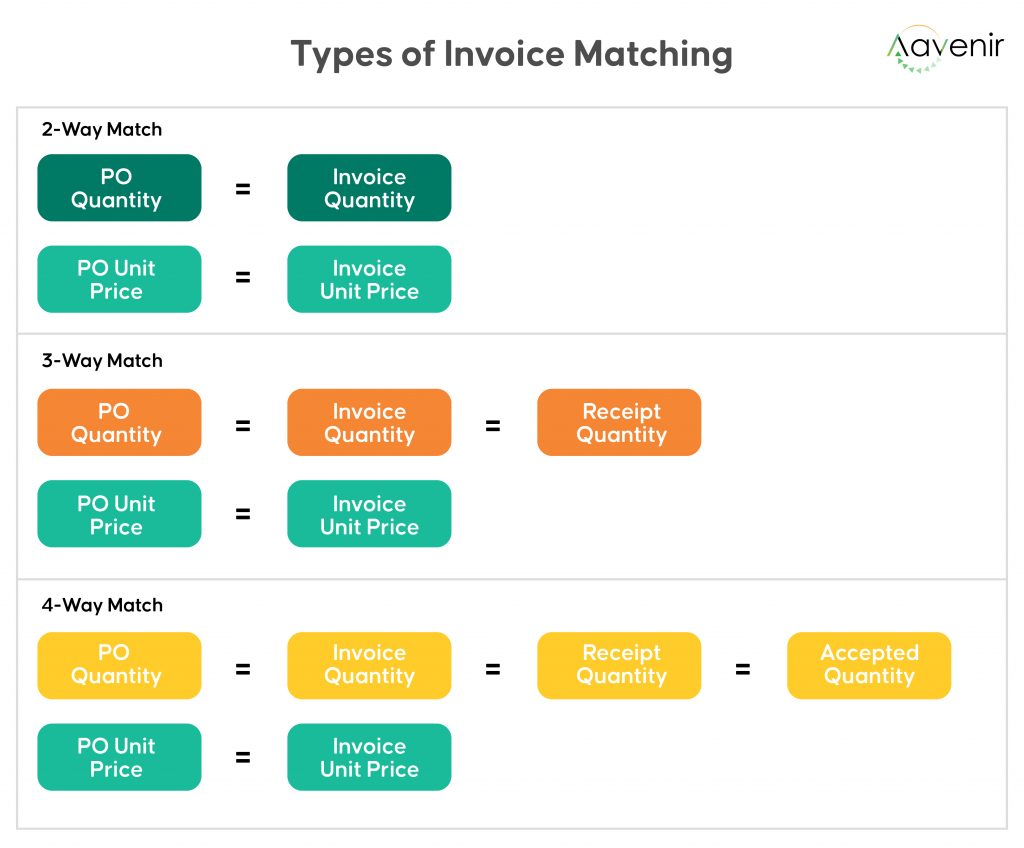
- At the first tier, 2-way matching is a simple comparison of invoice details with the original purchase order information.
- In 3-way invoice matching, the third layer verifies the invoice to the purchase order and the receipt supplied once the order has been filled and paid.
- Finally, 4-way matching incorporates all of the preceding. Furthermore, the invoice is matched to the acceptance or inspection document, which the recipient creates once the company receives the order.
The majority of businesses use 3-way invoice matching. it is essential to ensure that master data, such as vendor ledgers, purchase order details, and goods receipts can synchronize seamlessly between the ERP system and the AP automation solution to allow automatic 3-way invoice matching software.
Difference between Manual and Automated Invoice Processing
To properly illustrate the differences, let’s look at the steps required in each invoice processing method: –
Manual Invoice Processing Steps
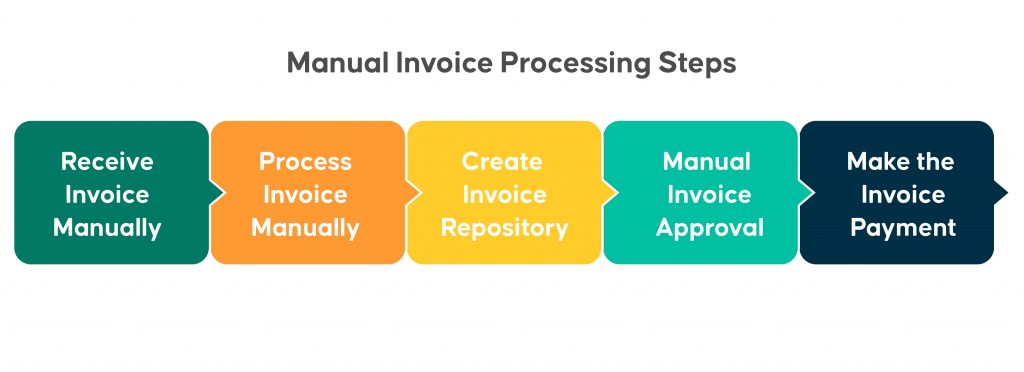
When all steps of the procedure are carried out manually, from receiving an invoice to the payment clearance, the process is referred to as manual invoice processing.
Step 1: Receiving invoice from the vendor – Receiving an invoice from the vendor is the first step. Depending on the terms of the contract, an invoice may be provided before or following the delivery of goods or services. After that, data is manually entered into the accounting system by the accounting team.
Step 2: Process the invoice against tolerances – The second stage, unique to PO invoices, is to process the invoice concerning tolerances. For pre-defined tolerances, the received invoice is processed using 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way match processing methods against the purchase order (PO).
Step 3: Create invoice repository – The invoice is scanned and stored safely in the filing system after being entered into the accounting system and processed against tolerances. Physical copies of invoices are frequently kept as well.
Step 4: Invoice approval – The invoice is sent for payment approval based on the size and structure of the company. In small organizations, one or two persons may have the authority and obligation to approve invoices for payment. In contrast, invoice approvals are the whole team’s responsibility in significant businesses and enterprises.
Is your organization still relying on manual invoice matching? Get in touch with our experts to know how you can boost efficacy for your AP teams with AP Automation – Built on ServiceNow.
Step 5: Make the invoice payment – Payment is made after the invoice has been accepted. Despite being time-consuming and requiring significant manual labor, this process is not flawless. Automated invoice processing simplifies the accounting system’s extraction of information from an invoice and simplifies validation and storage. It decreases manual efforts, lowers costs, and is more efficient and accurate than manual invoice processing.
Automated Invoice Processing Steps
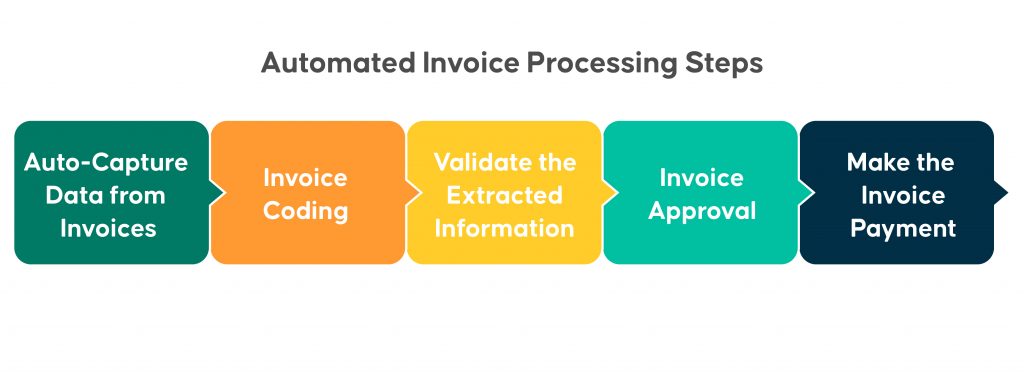
Step 1: Capture data from invoices – Invoices differ in appearance, structure, and fields, but an automated invoice capture tool easily integrates invoice data from paper invoices or electronic invoices delivered via Electronic Data Interchange using Intelligent OCR and machine learning technology.
Step 2: Invoice coding – Data entry and coding are accomplished by Intelligent Data Capture methods that recognize and collect data for processing into your invoice management system, which, depending on the capability of your solution, will only require minimal or no monitoring from your AP specialist.
Step 3: Validate the extracted information – The invoice processing solution validates the recorded data for pre-defined validation rules after data extraction and invoice coding. It is routed for manual verification if it does not fit the established criteria and any anomalies are discovered.
Step 4: Invoice approval – This is also a time-consuming phase because it necessitates complicated logical solutions and continual follow-up. In this phase, the Enterprise Resource Planning and Enterprise Content Management systems are typically utilized to manage notifications, follow-ups, and assign approval tasks.
Step 5: Make the invoice payment – Finally, payment is made following invoice approval.



