What is Decentralized Procurement? – Definition
In decentralized procurement, purchasing authority is delegated to local branches or sites. The branch/site managers have the power to make purchases based on the needs of their branch. Businesses with a diverse geographic footprint typically use the decentralized purchasing model since it can benefit the company’s long-term growth.
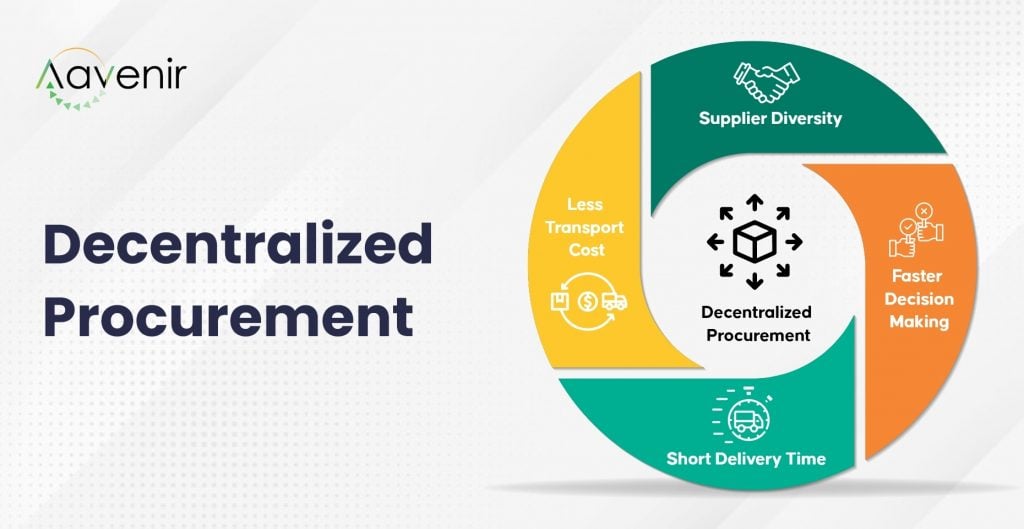
Advantages of Decentralized Procurement
Reduced bureaucracy
Decentralized procurement has less bureaucracy because the branch manager has total control over the branch’s spending and procurement process and reviews its operations and performance.
Effortless collaboration
The procurement unit is positioned in the operating site and may coordinate procurement activities on a regional level, which is one of the main advantages of having a decentralized process. Each department can readily purchase items on demand to suit short- and long-term needs. With fewer offices or departments to serve, the purchasing crew is considerably closer to the requesters, allowing them to understand the requirements better and purchase things at better pricing.
Local sources and suppliers
It’s challenging for a central team to find local suppliers for each branch when a company has a global presence with branches all over the world. As a result, the firm loses out on the advantages of working closely with local vendors. Decentralized purchasing allows for more personalized interactions between site staff and suppliers, resulting in lower prices, valuable customer bonuses, and cheaper transportation.
Accelerated purchasing process
The importance of timeliness in the purchase process cannot be overstated. Because purchasing units are available at each branch in this approach, the team can rapidly respond to the requester’s requirements. In the event of an emergency affecting a specific branch, the purchasing team is aware of the situation and can swiftly assist in mitigating the problems.
Decision-making is also faster in a decentralized model because the approval workflow is shorter, and communication between requesters and the purchasing team is substantially faster.
Conclusion
Organizations can utilize either a decentralized purchasing model, which allows each team or department to conduct its own procurement or a centralized procurement model, which handles purchasing for the entire firm. Various contributing elements decide whether a model is appropriate for a company. Making a decision on whether to use a decentralized procurement model necessitates a thorough examination of the firm’s surroundings, supply chain logistics, supplier relationships, and the needs of individual departments.
Explore Additional Resources To Know More