Contract payment terms form the financial backbone of every business relationship, yet they remain one of the most misunderstood and poorly managed aspects of commercial agreements. By clearly outlining financial obligations and expectations, these terms help prevent disputes, ensure timely payments, and foster positive collaboration.
For decision-makers, procurement teams, and legal professionals managing enterprise contracts, understanding how to structure, negotiate, and enforce payment terms can mean the difference between healthy cash flow and costly disputes.
This guide covers everything you need to know about contract payment terms—from basic definitions to advanced negotiation tactics and automation strategies.
What Are Contract Payment Terms?
Contract payment terms are the specific conditions that govern when, how, and under what circumstances payments must be made between contracting parties. These terms establish the financial framework for the entire business relationship, defining not just payment schedules but also the consequences of non-compliance, acceptable payment methods, and dispute resolution mechanisms. They’re the financial blueprint of your business agreements.
These terms typically include:
- Payment amounts and calculation methods
- Due dates and payment schedules
- Payment methods (wire transfer, check, ACH)
- Invoice requirements and submission procedures
- Late payment penalties and interest rates
- Dispute resolution processes
Think of payment terms as your financial safety net. Without them, you’re operating on assumptions that often lead to costly misunderstandings.
Types of contract payment terms
Net payment terms
The most common structure in B2B contracts. “Net 30” means payment is due 30 days after invoice receipt. Variants include Net 15, Net 45, Net 60, or Net 90, depending on industry standards and negotiation outcomes.
Milestone-based payments
Payments tied to specific project achievements. For example:
- 25% upon contract signing
- 50% at project midpoint
- 25% upon final delivery
This structure works well for long-term projects and reduces risk for both parties.
Advance payments
Partial or full payment before work begins. Common in manufacturing, custom services, or when working with new vendors. Protects suppliers but requires trust from buyers.
Progress payments
Regular payments throughout project duration, often monthly or quarterly. Ideal for ongoing services like consulting, maintenance, or subscription-based arrangements.
Retention payments
A percentage of total payment held until specific conditions are met—warranty periods expire, final acceptance occurs, or performance guarantees are satisfied.
Why Contract Payment Terms matter?
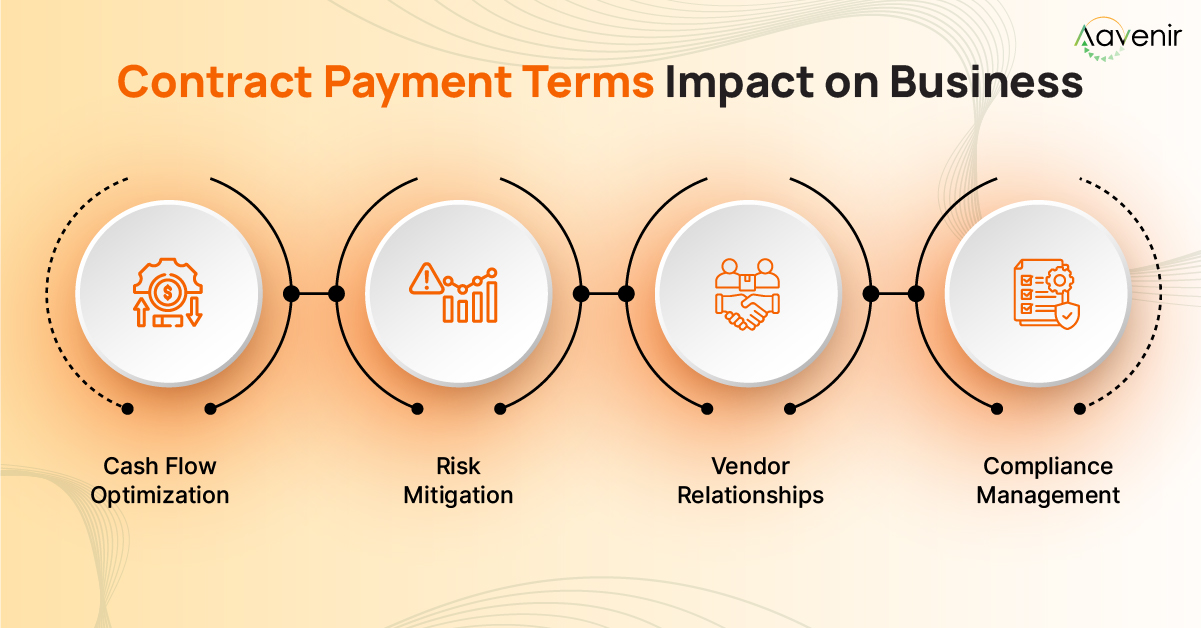
Cash flow predictability
Clear payment terms let you forecast when money enters and exits your business. This predictability enables better resource allocation, investment planning, and operational decisions.
Risk mitigation
Well-structured terms protect against non-payment, partial payment, and delayed payment scenarios. They also establish legal grounds for collection if disputes arise.
Vendor relationship management
Transparent payment expectations build trust between parties. When everyone understands their obligations upfront, partnerships become more sustainable.
Compliance protection
Different industries and jurisdictions have varying payment regulations. Proper terms ensure you meet legal requirements while protecting your interests.
Key elements of effective Contract Payment Terms
1. Payment amount and calculation
Specify the exact amount or calculation method. Options include:
- Fixed price: Single amount for entire scope
- Time and materials: Hourly rates plus expenses
- Cost-plus: Actual costs plus agreed markup
- Performance-based: Payment tied to measurable outcomes
2. Payment schedule
Define exactly when payments are due:
- Specific calendar dates
- Days after invoice receipt
- Project milestone completion
- Delivery and acceptance events
Avoid vague language like “reasonable time” or “prompt payment.”
3. Payment methods
Specify acceptable payment forms:
- Electronic funds transfer (fastest, lowest fees)
- Wire transfers (secure for large amounts)
- Checks (traditional but slower)
- Credit cards (convenient but higher fees)
For international contracts, specify currency and exchange rate terms.
4. Invoice requirements
Detail what invoices must include:
- Itemized descriptions of goods/services
- Contract reference numbers
- Correct billing addresses
- Required approval signatures
- Supporting documentation
5. Late payment provisions
Establish consequences for delayed payments:
- Interest rates (typically 1-2% per month)
- Flat late fees
- Service suspension rights
- Collection cost recovery
Negotiating better Contract Payment Terms
For buyers
- Extend payment periods while offering early payment discounts
- Request milestone structures that align with your budget cycles
- Negotiate volume discounts for larger commitments
- Include dispute resolution clauses to avoid costly litigation
For vendors
- Emphasize cash flow benefits of shorter payment terms
- Offer service guarantees tied to prompt payment
- Propose partial advance payments for significant projects
- Bundle payment terms with other valuable contract elements
Common negotiation points
- Payment timing vs. service levels
- Early payment discounts vs. extended terms
- Retention amounts vs. warranty periods
- Currency risk allocation in international deals
Sample Contract Payment Term Clauses
Standard net terms
“Payment is due within thirty (30) days of invoice receipt. Invoices must include detailed descriptions of services provided and correct contract references. Late payments incur 1.5% monthly interest on outstanding balances.”
Milestone-based structure
“Payments follow this schedule: (a) 30% upon contract execution, (b) 50% upon Phase 1 completion and written acceptance, (c) 20% upon final delivery. Each payment requires written acceptance within 10 business days.”
Early payment incentive
“Standard terms are Net 30. Client may deduct 2% from invoice amounts for payments received within 10 days of invoice date.”
International payment terms
“All payments in US Dollars via wire transfer to designated account. Currency conversion rates determined by [Bank Name] on payment date. Buyer responsible for all transfer fees.”
Automating Contract Payment Terms with CLM
Modern contract lifecycle management (CLM) systems transform payment term management from reactive administration into proactive business intelligence.
Key automation benefits
- Automated alerts before payment due dates
- Milestone tracking with automatic payment triggers
- Integration with accounting and procurement systems
- Compliance monitoring across entire contract portfolios
- Performance analytics to optimize future negotiations
Real-world impact
A global manufacturer managing 2,000+ supplier contracts reduced late payments by 75% after implementing CLM automation. Learn more about such contract management trends here. The system provided automated alerts, standardized payment terms, and gave finance teams accurate cash flow forecasting.
CLM systems help businesses regain control over contract payment terms by providing visibility into payment schedules and tracking compliance automatically.
Common Payment Term Mistakes

1. Vague language
Problem: Terms like “reasonable time” or “industry standard” provide no clear guidance.
Solution: Use specific timeframes and measurable criteria.
2. Missing late payment penalties
Problem: No consequences for delayed payments encourage slow payers.
Solution: Include reasonable interest rates and collection cost recovery.
3. Inconsistent terms across contracts
Problem: Different payment structures create administrative confusion.
Solution: Develop standardized templates while maintaining flexibility for unique situations.
4. Ignoring local regulations
Problem: Payment terms that violate local laws are unenforceable.
Solution: Research jurisdiction requirements before finalizing terms.
5. No modification procedures
Problem: Rigid terms can’t adapt to changing circumstances.
Solution: Include procedures for mutually agreed modifications.
Contract Payment Terms Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure your payment terms are comprehensive and enforceable:
Payment structure
- Specify exact payment amounts or calculation methods
- Define payment schedule (dates, milestones, or events)
- Choose appropriate payment methods
- Include currency specifications for international contracts
Invoice management
- Detail required invoice information
- Specify submission procedures and recipients
- Define approval processes and timeframes
- Include dispute resolution for invoice disagreements
Risk protection
- Set reasonable late payment penalties
- Include interest rates for overdue amounts
- Define rights for non-payment scenarios
- Establish collection cost recovery terms
Compliance and administration
- Verify terms comply with local regulations
- Include modification and amendment procedures
- Define record-keeping requirements
- Specify governing law and jurisdiction
Advanced Contract Payment Term Strategies
Performance-based payments
Link payments to measurable outcomes rather than just deliverables. This approach aligns incentives and can improve project results while protecting buyers from underperformance.
Dynamic payment terms
Adjust payment schedules based on performance metrics, volume thresholds, or market conditions. This flexibility can strengthen long-term partnerships while maintaining fair risk allocation.
Supply chain finance integration
Coordinate payment terms with supply chain financing programs, allowing suppliers to receive early payments through third-party financing while buyers maintain extended terms.
Conclusion
Contract payment terms directly impact your organization’s financial health, operational efficiency, and business relationships. The difference between well-structured and poorly defined terms can mean predictable cash flow versus constant payment stress.
Successful payment terms balance your organization’s needs with market realities while maintaining compliance and fostering strong partnerships. As business relationships become more complex and international, sophisticated payment term management becomes increasingly critical.
Key takeaways for better payment terms:
- Use specific, measurable language in all clauses
- Align payment schedules with your cash flow needs
- Include reasonable but enforceable penalties for late payment
- Leverage CLM technology for automated tracking and compliance
- Regular review and optimization ensure terms remain effective
Modern CLM platforms like Aavenir’s contract management software automate routine payment term management while providing strategic insights for continuous improvement. By combining well-crafted terms with smart technology, your contracts become valuable business assets that support sustainable growth and stronger partnerships.
Remember: effective payment terms aren’t just legal requirements—they’re strategic tools that can significantly improve your organization’s financial performance and competitive position.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can contract payment terms be changed after contract signing?
Yes, but only with written agreement from both parties and proper amendment procedures. Unilateral changes are generally unenforceable.
What’s the standard contract payment term for most industries?
Net 30 is most common in B2B transactions, but this varies by industry. Technology companies often use Net 15, while construction might use Net 45.
How do international payment terms handle currency fluctuations?
Specify the payment currency, exchange rate determination method, and which party bears currency risk. Consider hedging strategies for large, long-term contracts.
What happens if payment terms conflict with local laws?
Local regulations typically override contractual terms. Research applicable laws in all relevant jurisdictions before finalizing payment terms.
Should small businesses offer early payment discounts?
Early payment discounts (typically 1-3%) can improve cash flow and reduce collection costs, but ensure the discount doesn’t exceed your cost of capital.