Contracts are categorized in various ways to improve management, efficiency, and compliance throughout their lifecycle.
A practical and widely adopted approach to contract classification divides contracts into buy-side and sell-side types. Each type has distinct nuances that determine its use cases and handling procedures.
Despite their differences, buy-side and sell-side contracts also share key similarities.
Learning about those differences and similarities is essential to elevating the Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM) process. By doing so, enterprise teams can effectively mitigate risks, align contracts with broader business strategies, and maintain contract value over time.
This article will examine how buy-side and sell-side contracts vary and discuss practical strategies for teams to manage them efficiently.
What are Buy-Side Contracts?
Buy-side contracts are used when the company purchases goods or services from external vendors, suppliers, or service providers. These contracts outline the terms of procurement, such as pricing, delivery timeline, and quality requirements.
Their primary focus is accurately communicating the organization’s needs to the external partners, securing favorable deals, optimizing costs, and minimizing compliance risks in agreements.
The key stakeholders in buy-side contract management include procurement teams, finance departments, and legal advisors. Here’s what they do to elevate buy-side contract management processes:
| Department | Roles & Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Legal Teams |
|
| Procurement Teams |
|
| Finance Teams |
|
Four essential activities that maximize the value of buy-side contracts include:
- Negotiating favorable terms: Procurement teams continuously collaborate with vendors and suppliers to obtain the best quote and maximize returns
- Recognizing discounts: Buy-side contracts may include clauses that facilitate discounts for high-volume orders or early payment
- Managing expenses: Provisions within these contracts ensure financial control by defining tangible spending limits and cutting unnecessary costs
- Ensuring compliance: Such a contract type is crucial for holding external stakeholders accountable for delivering goods or services according to agreed terms
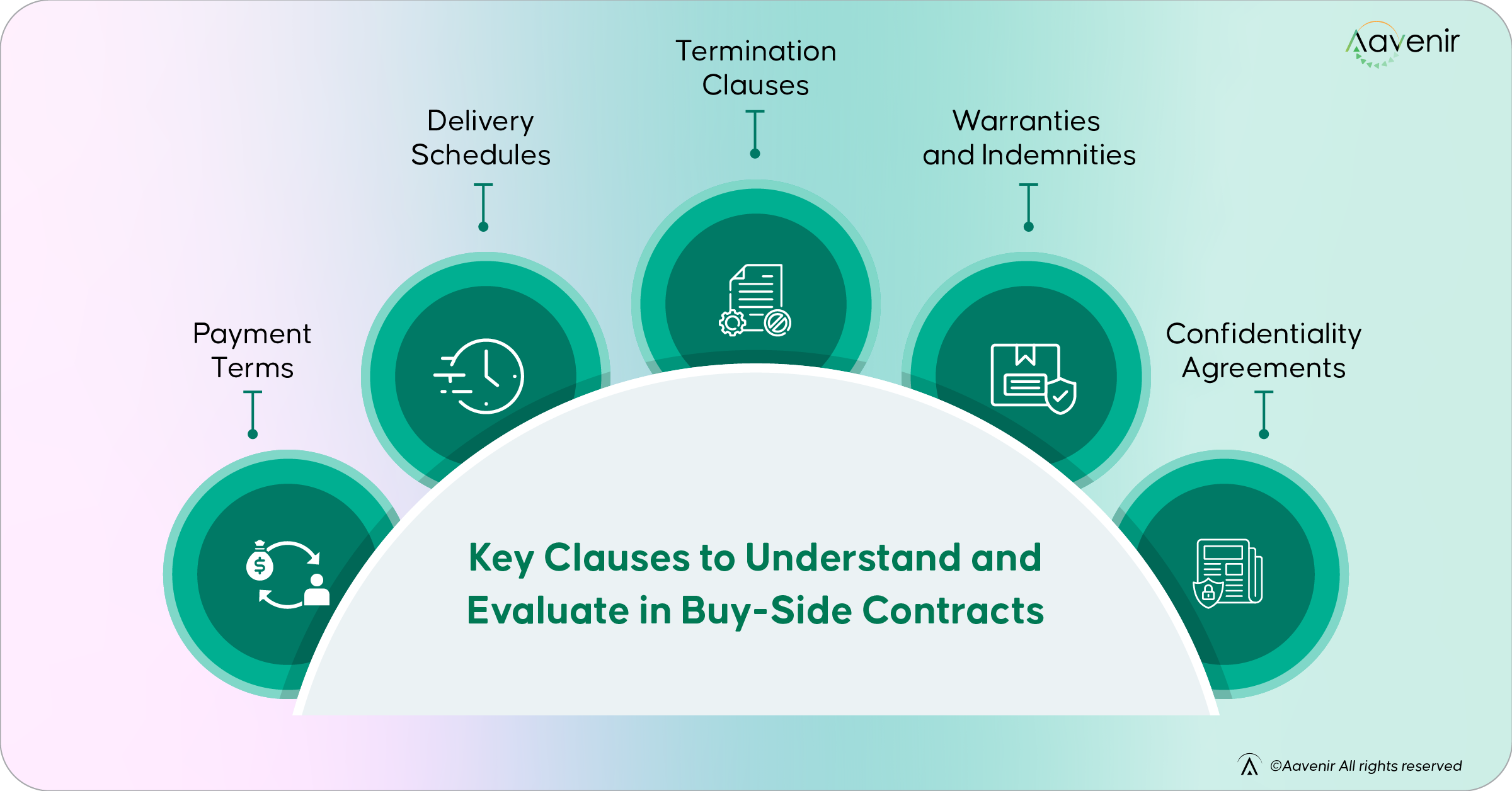
Key Clauses to Understand and Evaluate in Buy-Side Contracts:
- Payment terms: Timeline and conditions for monetary exchange
- Delivery schedules: Specifying when the products or services will be delivered or acquired
- Termination clauses: Conditions when the contract is deemed void or terminated
- Warranties and indemnities: Protecting the buyer from defective goods, services, and other liabilities
- Confidentiality agreements: Securing the organization’s sensitive information shared with the vendors and suppliers
What are Sell-Side Contracts?
Sell-side contracts are used when the company provides goods or services to its customers or clients. These agreements specify the terms of sale, including pricing, performance expectations, and delivery.
The broader objective of sell-side contracts is to generate revenue while fostering long-term trust-based relationships with buyers.
The key stakeholders executing sell-side contracts include sales teams, account managers, and legal departments. Their responsibilities in a sell-side contract management workflow include:
| Department | Roles & Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Sales Teams |
|
| Account Managers |
|
| Legal Departments |
|
The three critical business values brought by sell-side contracts include:
- Increased revenue: Sell-side contracts authenticate sales and hold the buyers accountable for payment for the goods and services sold
- Additional sales and upselling: Well-drafted sell-side contracts can create opportunities to increase the order or cart value
- Building trust: Clear and fair terms inspire customer confidence, enhancing the organization’s reputation and likelihood of repeat business
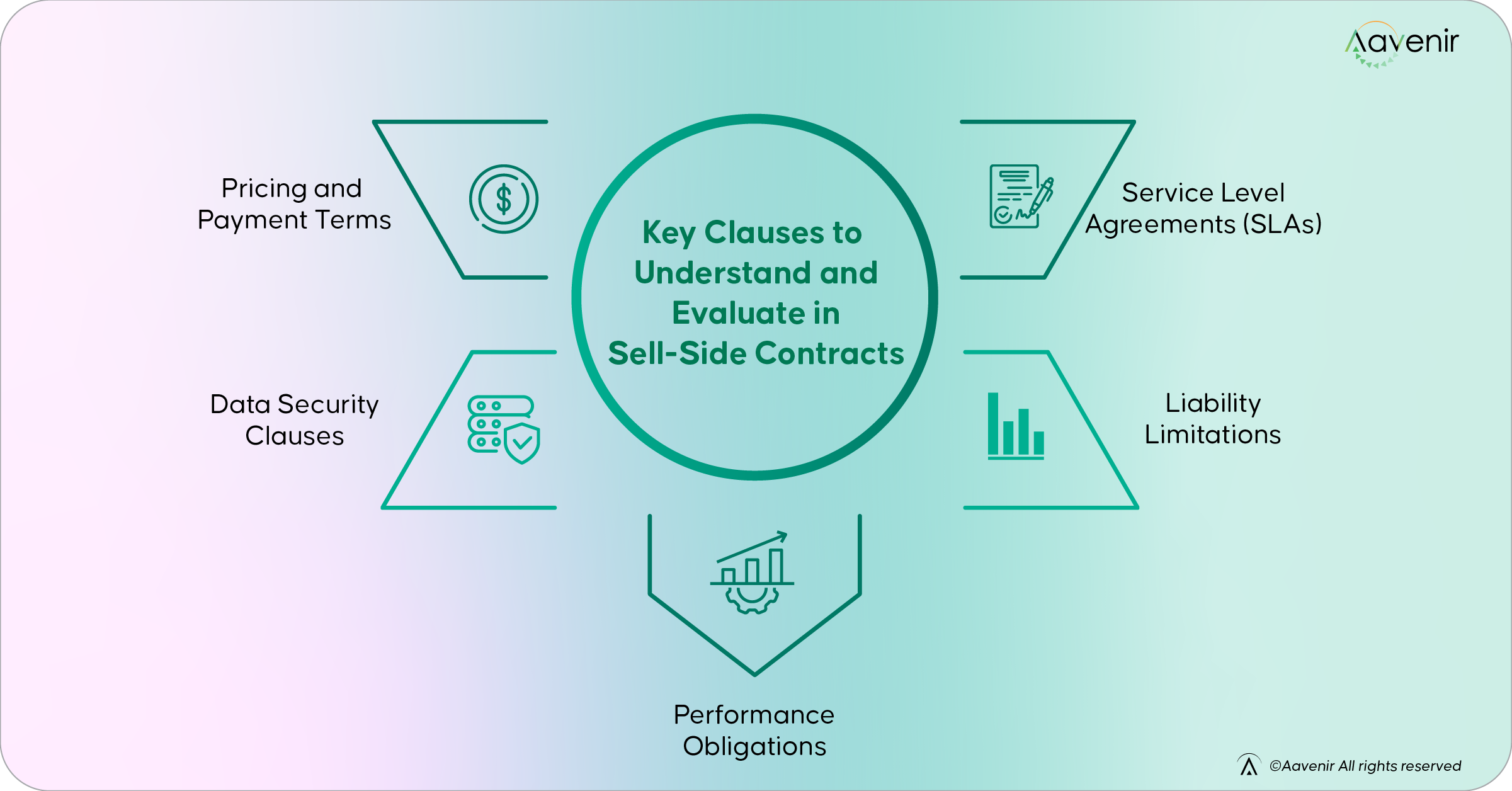
Key Clauses to Understand and Evaluate in Sell-Side Contracts:
- Pricing and payment terms: Outlining the monetary value of the goods or services and payment schedules or preferred methods
- Performance obligations: The quality of the deliverables and how they will fare in their respective use case
- Service level agreements (SLAs): Specifications of the goods and services, remedies for non-compliance, and resolution strategies
- Data security clauses: These inform customers about how their data will be used while protecting the company’s sensitive data
- Liability limitations: Securing the enterprise against excessive refund demands for losses and damages by limiting the amount a party can claim in case of loss or damages
Similarities Between Buy-Side and Sell-Side Contracts
While both contract types serve different purposes and bring unique value to the business, they share certain commonalities. These similarities are structural, considering both of them are, well, contracts.
Recognizing these areas of overlap will assist contract management teams in enterprises in streamlining their CLM workflows further.
Lifecycle Phases
Buy-side and sell-side contracts undergo initiation, negotiation, execution, performance monitoring, and closure. Each phase requires professionals to work in cross-functional teams.
Moreover, a similar degree of meticulous oversight throughout the lifecycle for either contract is necessary to ensure the agreement serves its intended purpose.
For instance, stakeholders establish terms during the initiation and negotiation stages that achieve business objectives, such as cost savings (buy-side) or revenue optimization (sell-side).
Need for Compliance and Legal Considerations
Legal teams in enterprises and large corporations must ensure that both contract types adhere to regulatory standards. This includes public policy, industry-specific guidelines, and any additional organizational standards.
Non-compliance to any set of laws in buy-side and sell-side contracts can lead to financial penalties, loss of stakeholder confidence, and reputational damage. The relevant legal terms also protect all parties through clauses like confidentiality, indemnity, and termination.
Importance of Relationship Management
Buy-side contracts nurture productive supplier relationships and sell-side contracts focus on building trust with customers and clients. Both contract types achieve this by ensuring the parties collaborate transparently and respecting the agreed terms.
Additionally, enterprises can centralize contract performance tracking to strengthen these relationships further.
Differences Between Buy-Side and Sell-Side Contracts
Buy-side and sell-side contracts differ based on the purpose served, risks, and performance metrics. These distinctions shape how these agreements are handled by the relevant stakeholders.
Objectives
The primary objective of a buy-side contract is to reduce costs while securing the necessary resources for business operations. Procurement teams negotiate favorable terms and acquire quality goods or services cost-effectively.
Sell-side contracts aim to maximize revenue and capture a larger market share. The sales team achieves it by highlighting the value for customers and strengthening buyer relationships to ensure long-term loyalty.
Risk Management Focus
The risks of buy-side contracts include delays, quality issues, and surprise expenses during acquisition or purchase. Relevant clauses and relationship management manage this supplier’s reliability and compliance risks.
For sell-side contracts, the common risks include service level breaches, delayed deliveries, or disputes due to customer dissatisfaction. These are handled by focusing on customer satisfaction and fulfillment to ensure the buyers get what they signed up for.
Performance Metrics
Supplier performance metrics determine the efficacy of a particular buy-side contract. The key performance indicators (KPIs) include cost savings, quality adherence, timeliness, and compliance rates monitored and iteratively optimized by procurement teams.
The KPIs that denote the impact of sell-side contracts include sales targets, retention rates, and revenue growth. Various stakeholders, such as sales teams and account managers, own these metrics and audit the relevant processes to optimize them.
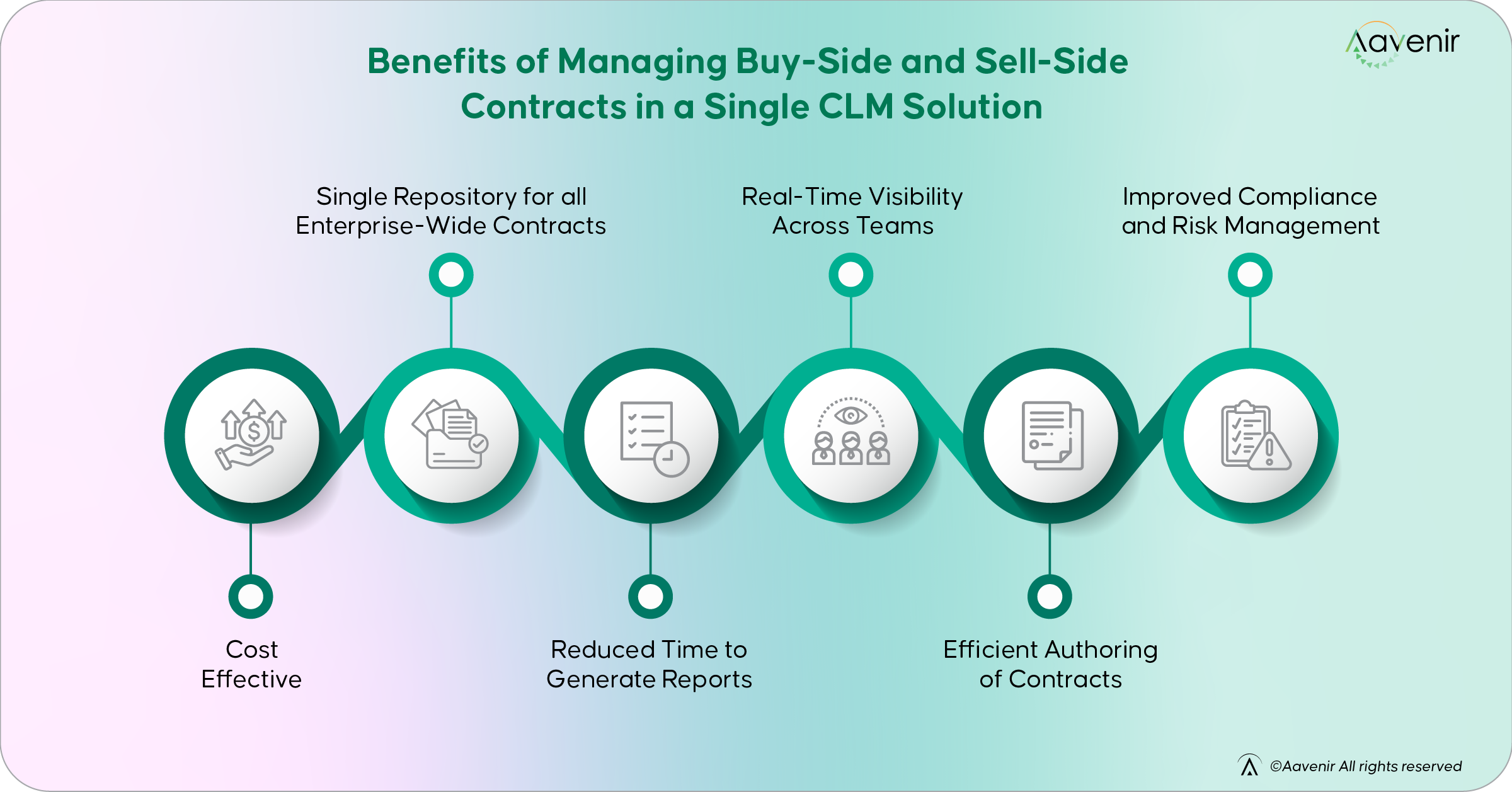
Benefits of Managing Buy-Side and Sell-Side Contracts in a Single CLM Solution
The differences between buy-side and sell-side contracts may motivate enterprises to manage the corresponding CLM workflows in separate software.
However, while it may appear logical, the opposite — managing both contract types in a single CLM solution — is significantly better.
1. Cost-Effective
Leveraging a unified CLM solution to manage both types of contracts eliminates the need to pay for two distinct enterprise platforms. Teams can save big because they will pay for a single platform, simplifying budgeting.
Moreover, this eliminates silos, primarily when a particular team handles buy-side and sell-side contracts simultaneously. This translates to productive processes, streamlining operations further to save resources.
2. Single Repository for All Enterprise-Wide Contracts
A consolidated solution serves as the single source of truth for all associated stakeholders.
Teams can avoid juggling multiple tools to find information and duplicating effort. Contract managers can have complete visibility over the CLM processes to streamline daily operations.
Additionally, this enhances transparency across departments. Various professionals can access the latest contract information in real-time.
3. Reduced Time to Generate Reports
Industry-leading enterprise-grade CLM solutions like Contractflow offer customizable dashboards and automated reporting capabilities. Thus, organizations can quickly extract and compile necessary data.
This also unlocks strategic insights. Teams can make more accurate cost estimations and sales forecasts, and this information can be shared with stakeholders to improve visibility further.
4. Real-Time Visibility Across Teams
Organizations can access contract documents, key terms, standardized templates, pre-approved clauses, and contract performance data. This helps enterprises to democratize information and keep efforts aligned.
Moreover, real-time visibility and transparency allow contract teams to be more agile and responsive to changing requirements. Whether it is a new vendor request or an evolving market trend, tweaking the CLM process to adapt will be easier.
5. Efficient Authoring of Contracts
Contract creation could take hours, especially when managed with different tools.
A single repository of pre-approved templates and clauses for different occasions can expedite contract authoring. It is also beneficial in ensuring consistency and compliance while saving time during the review and feedback stages.
Additionally, teams can build custom workflows with rule-based automation to offload administrative tasks such as quickly sending updates and changing contract status. Conversely, using two separate CLM software will require duplication of effort while building and managing such automation over time.
6. Improved Compliance and Risk Management
With unified solutions, enterprise contract teams can embed compliance checks into their buy-side and sell-side CLM workflows. The software can flag non-compliant clauses, track jurisdiction-based regulations, and record document version histories.
On the other hand, using separate tools for each type of contract may cause organizations to lose time inserting standard compliance clauses and policies. This repetition of effort could cost contract teams hours.
The Unified CLM Solution for Buy-Side and Sell-Side Contract Management
Aavenir Contractflow is a unified CLM solution enabling enterprise teams to manage buy-side (procurement) and sell-side (supplier) contracts.
The AI-enabled platform standardizes and automates various processes in the contract lifecycle to streamline management.
The capabilities that make it possible include:
- Contract authoring and management: Aavenir Contractflow’s self-service contract authoring tool allows organizations to create agreements efficiently with templates and pre-approved clauses.
- AI-powered features:
- Extracting metadata and clauses from contracts in natural language
- Clause deviation recommendations to ensure accuracy
- Generative AI assistant (Avy AI) that can generate clauses, write contract summaries, and more
- Contract lifecycle workflows: Automate various stages within the contract lifecycle, such as negotiation, approval, and execution for buy-side and sell-side agreements.
- eSignature support: Aavenir seamlessly works with Adobe Sign and DocuSign to ensure the legality of the authorizations and approvals.
- Robust integrations: Organizations can connect Aavenir with other enterprise tools to manage either type of contract, such as SAP, Salesforce, and Oracle.
- Advanced reporting: Get over 30 ready-to-export contract reports to extract actionable insights to improve buy-side and sell-side CLM processes.
In addition, teams can use Aavenir to track obligations, manage vendor relationships, and collaborate with stakeholders.
Interested in learning how Aavenir can revolutionize your CLM workflows?
Contact us today to book a personalized demo.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between buy-side and sell-side contracts?
Buy-side contracts involve procuring goods or services from suppliers, focusing on cost savings and compliance. Sell-side contracts govern the sale of goods or services to customers, prioritizing revenue generation and customer satisfaction.
2. Why is effective management of buy-side and sell-side contracts crucial for enterprises?
Effective management ensures cost efficiency, risk mitigation, compliance, and streamlined operations. It also strengthens supplier and customer relationships, aligning contract outcomes with organizational goals and enhancing business performance.
3. How can automation improve the efficiency of contract management?
Automation reduces manual tasks, accelerates workflows, and ensures consistency in processes. It enhances accuracy in contract creation, compliance tracking, and reporting, enabling teams to focus on strategic decision-making and value-driven initiatives.
4. How does a unified contract management system benefit large businesses?
A unified system centralizes all contracts, streamlines workflows, improves visibility across teams and simplifies compliance management. It reduces costs, enhances collaboration, and provides real-time insights for better decision-making and operational alignment.